
Đề thi IELTS bao gồm 4 phần thi:
- Nghe – IELTS Listening Test: 30 phút
- Đọc – IELTS Reading Test: 60 phút
- Viết – IELTS Writing Test: 60 phút
- Nói – IELTS Speaking Test: 11-15 phút.
Bạn sẽ thi từng kỹ năng Listening, Reading, Writing trong cùng một ngày.
Riêng Speaking bạn có thể nhận được lịch thi trước hoặc sau hoặc có thể cùng ngày với 3 kỹ năng kia.
Trong bài viết này, IELTS Fighter sẽ chia sẻ cấu trúc 4 phần thi IELTS cho các bạn hi vọng sẽ giúp ích cho các bạn trong quá trình ôn thi hiệu quả nhé! Và có thay đổi về Listening trong năm 2020.
Cấu trúc đề thi IELTS chi tiết
Trước khi đi tìm hiểu cấu trúc bài thi IELTS chuẩn với 4 phần test như trên thì bạn cần biết về hai loại hình thức thi của nó.
1. Hai hình thức thi IELTS
– Bài thi IELTS có 2 hình thức là : IELTS Academic ( Học thuật) và IELTS General Training ( Tổng quát).
Trong đó, bài thi Academic dành cho các bạn có nhu cầu thi lấy bằng IELTS để apply học tập vào các trường đại học, cao đẳng, viện nghiên cứu…tại các nước sử dụng ngôn ngữ này trên thế giới. Nhưng bằng Academic cũng dùng được trong trường hợp học tập và làm việc, định cư khác.
Bài thi General dành cho những ai muốn thi để xin việc, định cư, làm việc, sinh sống tại môi trường quốc tế.
– Vì sự khác biệt giữa hai bài thi này mà cấu trúc đề thi IELTS của hai hình thức cũng khác nhau, các bạn đọc kỹ dưới đây để biết chi tiết.
– Dạng cấu trúc bài thi IELTS Academic và General Training sẽ có phần thi Nghe và Nói tương tự nhau phần Đọc và Viết sẽ khác nhau ở một vài phần.
Các bạn có thể xem bảng thời gian và cấu trúc bàithi IELTS dưới đây đồng thời đọc phần phân tích dưới để hiểu rõ hơn:
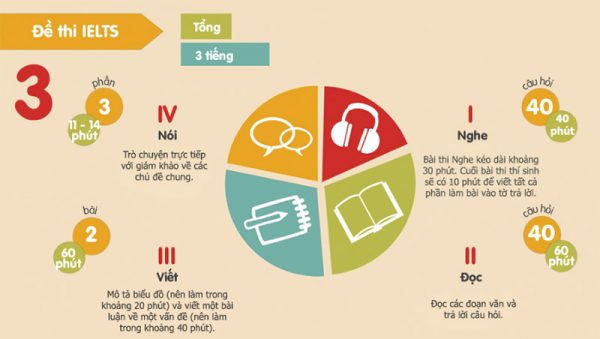
2. Cấu trúc đề thi Listening
– Thời gian thi: 40 phút
– Cấu trúc bài thi listening bạn sẽ được nghe 4 đoạn hội thoại ghi âm gồm có: độc thoại, đàm thoại bởi một số người bản xứ có thể 2 hoặc nhiều người có giọ
ng phát âm khác nhau của nhiều quốc gia khác. Các đoạn hội thoại sẽ có độ khó tăng dần.
– Phần 1: Chủ đề đoạn hội thoại xoay quanh tình huống về cuộc sống, đó là cuộc đàm thoại giữa hai người. Ví dụ có thể là cuộc nói chuyện người bán hàng và mua hàng tại một siêu thị nhỏ.
– Phần 2: một đoạn độc thoại trọng ngữ thường ngày, đó có thể là các tình huống hướng dẫn và giới thiệu 1 chủ đề quen thuộc như du lịch, trường học…
– Phần 3. Đây sẽ là buổi đàm thoại giữa 3 người hoặc bốn người chủ đề xoay quanh giáo dục, ví dụ có thể thảo luận về bài tập trên lớp.
– Phần 4. Thí sinh sẽ được nghe đoạn độc thoại từ một người bản xứ có thể đang giảng bài hay thuyết trình về vấn đề gì đó? Đoạn hội thoại này mang tính học thuật cao.
Người thi sẽ có thời gian nghe là 30 phút và bạn chỉ được nghe 1 lần duy nhất. Tuy nhiên trước đó bạn có khoảng thời gian ngắn để đọc câu hỏi, suy đoán câu trả lời. Kết thúc 4 bài nghe các bạn sẽ có 10 phút để điền lại đáp án vào tờ answer sheet.
Lưu ý: Cập nhật một số thay đổi mà IELTS Official vừa công bố về cấu trúc đề thi IELTS Listening nhé.
Cụ thể, các thay đổi này sẽ được thực hiện từ ngày 4 tháng 1 năm 2020, bao gồm:
– Các bài trong bài Listening sẽ không được gọi là Section nữa mà sẽ được gọi là Part. Số lượng bài nghe vẫn là 4 như bình thường.
– Trong phần mở đầu bài thi ở Section 1 (giờ là Part 1), thí sinh sẽ không được nghe ví dụ thực hiện bài làm như trước nữa.
– Trong mỗi bài, hướng dẫn cho thí sinh sẽ không đề cập cụ thể số trang trên đề nữa (Ví dụ như mở trang 2 trong đề và nhìn vào hình vẽ ABC nào đó chẳng hạn)
Ngoài ra thì nội dung bài thi Listening vẫn sẽ giữ nguyên.
Tuy đây chỉ là một số thay đổi nhỏ về hình thức trình bày bài thi, các bạn cũng cần phải ghi nhớ chúng để quen dần với cách thức đề bài mới nhất nhé.
3. Cấu trúc đề thi Reading
– Thời gian thi: 60 phút
– Trong 60 phút thí sinh phải hoàn thành 40 câu hỏi.
– Cấu trúc đề thi Reading Academic và General Training sẽ có một vài phần khác biệt như sau:
– Đối với Học thuật:
Bài thi có 3 đoạn văn, độ dài tầm 1500 từ, độ khó tăng dần. Các đề đa phần được trích dẫn từ sách, báo, tạp chí… các đoạn văn được chọn dành cho đọc giả mang tính chất chuyên môn cao.
– Đối với dạng không Học thuật:
Các bài đọc được lấy nguồn từ sách, tạp chí, thông báo, quảng cáo … với độ dài các bài khác nhau, thường từ 700 – 1500 từ.
Tất cả tài liệu mà các bạn sẽ dễ bắt gặp trong môi trường sử dụng tiếng Anh hằng ngày, mục đích là kiểm tra trình độ hiểu và các xử lý thông tin của ứng viên thi IELTS.
4. Cấu trúc đề thi Writing
– Thời gian thi: 60 phút
– Cấu trúc bài thi IELTS Writing gồm 2 bài Task 1 và Task 2. Số chữ quy định Task 1 là 150 từ và task 2 là 250 từ.
– Đối với học thuật ( Academic) :
Task 1: Thí sinh được yêu cầu viết bài báo cáo khoảng 150 từ để mô tả, giải thích dữ liệu của một biểu đồ, bảng biểu hay quy trình…
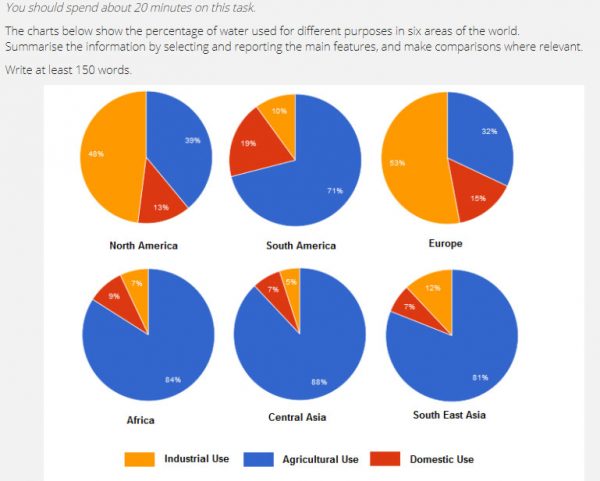
Task 2: Bạn cần viết bài luận 250 từ, đưa ra những ý kiến chiến tranh luận về 1 ý kiến và hoặc vấn đề xã hội.

– Đối với dạng không học thuật ( Genaral Training)
Task 1: Thí sinh được yêu cầu viết bức thư chính thức hoặc không chính thức khoảng 150 từ với mục đích hỏi thăm thông tin hoặc giải thích tình huống trong cuộc sống.

Task 2: Bạn được yêu cầu viết bài luận 250 từ phản hồi lại quan điểm, vấn đề nào đó. Bạn cần đưa ra những chính kiến của bản thân.

Như vậy, đề thi Writing của hai hình thức chủ yếu chỉ khác nhau ở phần Task 1 và Task 2 thì tương tự nhau với các đề thảo luận, nêu ý kiến…theo topic được đưa ra.
5. Cấu trúc đề thi Speaking
– Thời gian thi: 11-15 phút
– Đối với cả IELTS Academic và IELTS Genaral Training thì cấu trúc bài thi Speaking giống nhau. Phần thi nói của bạn có thể được diễn ra trước, sau hoặc cùng ngày thi với 3 kỹ năng trên.
– Bạn sẽ trò chuyện trực tiếp với giám khảo, thời gian thi bạn chỉ khoảng 11 – 14 phút và gồm có 3 phần thi. Các phần thi của bạn đều được ghi âm lại để đánh giá kết quả.
– Part 1: Đây được coi là phần khởi động cho bài thi Speaking, bạn sẽ nhận được các câu hỏi tương đối dễ xoay quanh các chủ đề về cuộc sống của bạn, gia đình, bạn bè, công việc, học tập….
– Part 2: Thí sinh được trao một mẩu giấy và cây bút và yêu cầu nói về một chủ đề cụ thể trong vòng tối đa 2 phút. Trước khi nói các bạn sẽ có 1 phút để chuẩn bị trước, sau đó giám khảo sẽ hỏi thêm 1 số câu hỏi về chủ đề này và kết thúc chuyển sang Part 3.
– Part 3: Bạn sẽ được hỏi thêm một số câu hỏi có thể liên quan đến chủ đề phần 2 hoặc không? Bạn cần phải thảo luận nhiều hơn với giám khảo để có thể gây ấn tượng tốt.
Lưu ý: Bạn không nên nói lặp lại các câu trả lời trước đã trình bày, hoặc lấy lại nguyên câu trong câu hỏi đưa ra.
——————————————————–
The IELTS test assesses your abilities in listening, reading, writing and speaking – in less than three hours.
There are two types of IELTS: Academic and General Training. Listening and Speaking are the same for both tests, but the subject matter of the Reading and Writing sections differs depending on which test you take.
The Listening, Reading and Writing sections of all IELTS tests are completed on the same day, with no breaks in between them.
The Speaking section, however, can be completed up to a week before or after the other tests. Your test centre will advise.
The total test time is 2 hours and 45 minutes.
Test format – Listening
30 minutes
You will listen to four recordings of native English speakers and then write your answers to a series of questions.
- Recording 1 – a conversation between two people set in an everyday social context.
- Recording 2 – a monologue set in an everyday social context, e.g. a speech about local facilities.
- Recording 3 – a conversation between up to four people set in an educational or training context, e.g. a university tutor and a student discussing an assignment.
- Recording 4 – a monologue on an academic subject, e.g. a university lecture.
Assessors will be looking for evidence of your ability to understand the main ideas and detailed factual information, the opinions and attitudes of speakers, the purpose of an utterance and evidence of your ability to follow the development of ideas.
IELTS Listening description
| Paper format | From 4 January 2020, some small changes were introduced to the instructions and layout of the paper-based Listening test:
There are four parts with ten questions each. The questions are designed so that the answers appear in the order they are heard in the audio. The first two parts deal with situations set in everyday social contexts. In Part 1, there is a conversation between two speakers (for example, a conversation about travel arrangements), and in Part 2, there is a monologue in (for example, a speech about local facilities). The final two parts deal with situations set in educational and training contexts. In Part 3, there is a conversation between two main speakers (for example, two university students in discussion, perhaps guided by a tutor), and in Part 4, there is a monologue on an academic subject. The recordings are heard only once. They include a range of accents, including British, Australian, New Zealand, American and Canadian. |
|---|---|
| Timing | Approximately 30 minutes (plus 10 minutes transfer time). |
| No. of questions | 40 |
| Task types | A variety of question types are used, chosen from the following: multiple choice, matching, plan/map/diagram labelling, form/note/table/flow-chart/summary completion, sentence completion. |
| Answering | Test takers write their answers on the question paper as they listen and at the end of the test are given 10 minutes to transfer their answers to an answer sheet. Care should be taken when writing answers on the answer sheet as poor spelling and grammar are penalised. |
| Marks | Each question is worth 1 mark. |
IELTS Listening in detail
A detailed look at the paper with links to related resources.
Task type 1 – Multiple choice
| Task type and format | In multiple choice tasks, there is a question followed by three possible answers, or the beginning of a sentence followed by three possible ways to complete the sentence. Test takers are required to choose the one correct answer – A, B or C.
Sometimes, test takers are given a longer list of possible answers and told that they have to choose more than one. In this case, they should read the question carefully to check how many answers are required. |
|---|---|
| Task focus | Multiple choice questions are used to test a wide range of skills. The test taker may be required to have a detailed understanding of specific points or an overall understanding of the main points of the listening text. |
| No. of questions | Variable |
Task type 2 – Matching
| Task type and format | Test takers are required to match a numbered list of items from the listening text to a set of options on the question paper. The set of options may be criteria of some kind. |
|---|---|
| Task focus | Matching assesses the skill of listening for detail and whether a test taker can understand information given in a conversation on an everyday topic, such as the different types of hotel or guest house accommodation. It also assesses the ability to follow a conversation between two people. It may also be used to assess test takers’ ability to recognise relationships and connections between facts in the listening text. |
| No. of questions | Variable |
Task type 3 – Plan, map, diagram labelling
| Task type and format | Test takers are required to complete labels on a plan (eg of a building), map (eg of part of a town) or diagram (e.g. of a piece of equipment). The answers are usually selected from a list on the question paper. |
|---|---|
| Task focus | This type of task assesses the ability to understand, for example, a description of a place, and to relate this to a visual representation. This may include being able to follow language expressing spatial relationships and directions (e.g. straight on/through the far door). |
| No. of questions | Variable |
Task type 4 – Form, note, table, flow-chart, summary completion
| Task type and format | Test takers are required to fill in the gaps in an outline of part or of all of the listening text. The outline will focus on the main ideas/facts in the text. It may be: 1. a form: often used to record factual details such as names 2. a set of notes: used to summarise any type of information using the layout to show how different items relate to one another 3. a table: used as a way of summarising information which relates to clear categories – e.g. place/time/price, 4. a flow-chart: used to summarise a process which has clear stages, with the direction of the process shown by arrows.Test takers may have to select their answers from a list on the question paper or identify the missing words from the recording, keeping to the word limit stated in the instructions. Test takers do not have to change the words from the recording in any way.Test takers should read the instructions very carefully as the number of words or numbers they should use to fill the gaps will vary. A word limit is given, for example, ‘NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER’. Test takers are penalised for writing more than the stated number of words, and test takers should check this word limit carefully for each task. Contracted words will not be tested. Hyphenated words count as single words. |
|---|---|
| Task focus | This focuses on the main points which a listener would naturally record in this type of situation. |
| No. of questions | Variable |
Task type 5 – Sentence completion
| Task type and format | Test takers are required to read a set of sentences summarising key information from all the listening text or from one part of it. They then fill a gap in each sentence using information from the listening text. A word limit is given, for example, ‘NO MORE THAN ONE WORD AND/OR A NUMBER’.
Test takers are penalised for writing more than the stated number of words. (Test takers should check this word limit carefully for each task: the limit is either ONE, TWO or THREE words). Contracted words will not be tested. Hyphenated words count as single words. |
|---|---|
| Task focus | Sentence completion focuses on the ability to identify the key information in a listening text. Test takers have to understand functional relationships such as cause and effect. |
| No. of questions | Variable |
Task type 6 – Short-answer questions
| Task type and format | Test takers are required to read a question and then write a short answer using information from the listening text. A word limit is given, for example, ‘NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER’. Test takers are penalised for writing more than the stated number of words. (Test takers should check this word limit carefully for each task.) Contracted words will not be tested. Hyphenated words count as single words. Sometimes test takers are given a question which asks them to list two or three points. |
|---|---|
| Task focus | Sentence completion focuses on the ability to listen for concrete facts, such as places, prices or times, within the listening text. |
| No. of questions | Variable |
IELTS Listening – how it’s marked
The Listening test is marked by certificated markers, who are regularly monitored to ensure their reliability. All answer sheets, after being marked, are further analysed by Cambridge Assessment English.
Band score conversion
A Band Score conversion table is produced for each version of the Listening test which translates scores out of 40 into the IELTS 9-band scale. Scores are reported in whole bands and half bands.
One mark is awarded for each correct answer in the 40-item test. Care should be taken when writing answers on the answer sheet as poor spelling and grammar are penalised.








